The Black Health & Wellness Pioneers series for Black History Month is an enlightening and inspirational journey through time that recognizes and celebrates Black individuals’ invaluable contributions to the health and wellness field. Within this series, we delve into the stories and achievements of prominent Black figures who have made significant strides in the realms of medicine, healthcare, fitness, mental health, and holistic wellness.
As our community knows, Sickle cell disease greatly affects Black people. According to the CDC, 1 in 13 Black or African-American babies is born with sickle cell trait (SCT), and SCD occurs among about 1 out of every 365 Black or African-American births. SCD is an inherited blood disorder that results in chronic anemia and recurring episodes of pain. In a person with SCD, some blood cells take on a sickle-like, crescent shape, causing hemoglobin to clump and block the capillaries, ultimately damaging blood-starved tissues. Over time, it can cause weakness, even death, especially for patients in developing nations, where treatment is not readily available. According to the Sickle Cell Disease Association of America, each year, approximately a thousand babies are born with the disease in America. While there have been recent advancements in research to expand treatments, there was a Black woman at the helm of the studies, Dr. Marilyn Hughes Gaston.
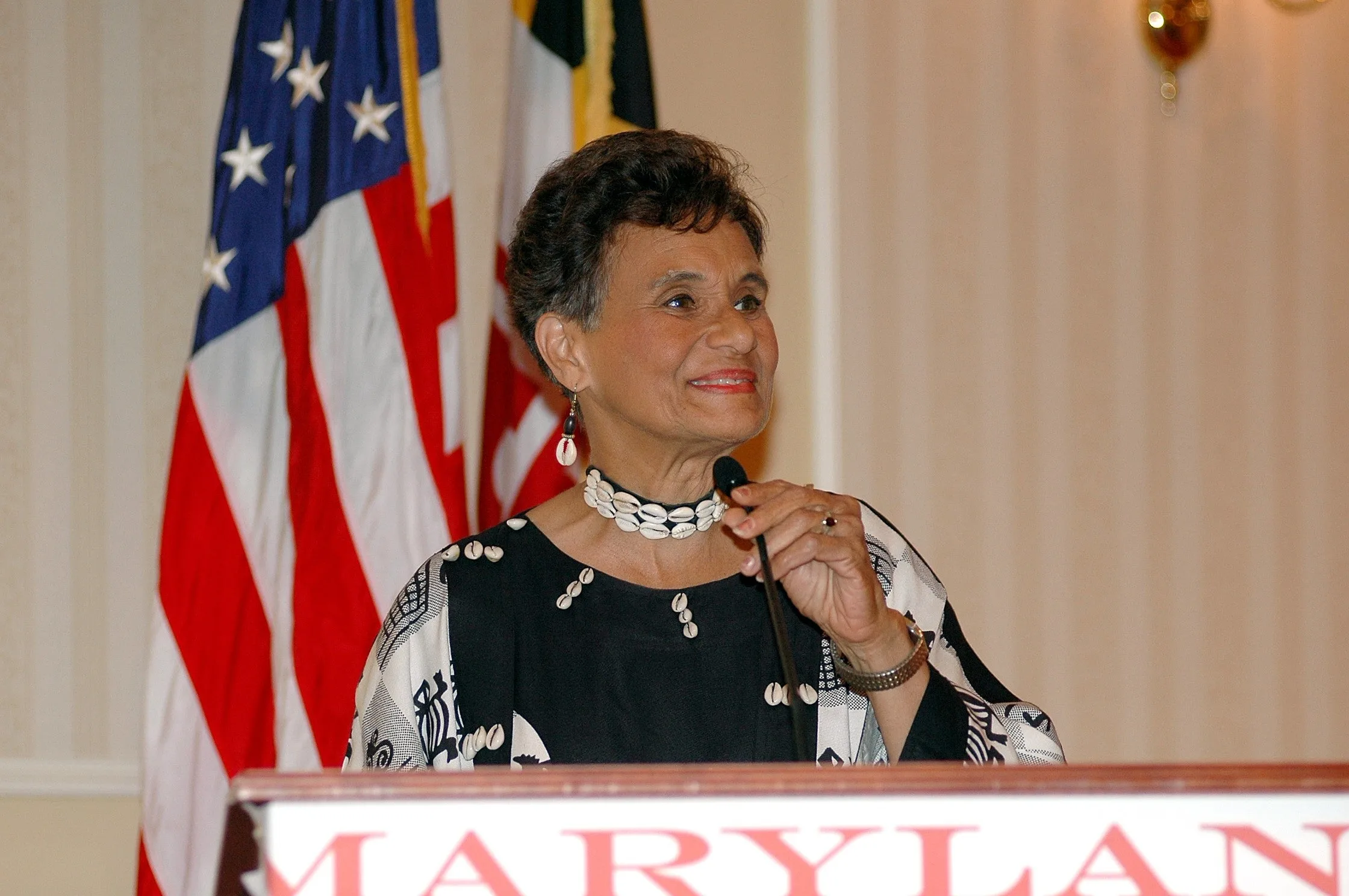
Marilyn Hughes Gaston, M.D., faced several adversities, like poverty and prejudice, as a young student but had her heart set on becoming a physician. She has dedicated her career to medical care for poor and minority families and campaigns for healthcare equality for all Americans. Her 1986 study of sickle-cell disease led to a nationwide screening program to test newborns for immediate treatment, and she was the first African American woman to direct a public health service bureau (the Bureau of Primary Health Care in the United States Department of Health and Human Services).
When she was 9 years old, Marilyn Hughes knew she wanted to be a doctor, but because of her socioeconomic status, she was dissuaded from pursuing her dream. She ultimately studied zoology at Miami University, and when she graduated in 1960, she enrolled at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, encouraged by a physician she worked for. When she began medical school, she was one of only six women and the only African-American woman in her year.
Dr. Gaston became interested in children with sickle cell disease (SCD) while doing her internship at Philadelphia General Hospital in 1964. According to the National Health Institutes of Health, one evening during her internship, Dr. Gaston admitted a baby with a badly swollen hand. No trauma was reported, and she could not find the cause of the swelling. Her supervising resident suggested she check the blood work for evidence of sickle cell disease. The child did have SCD, and his hand was swollen from infection. Gaston was appalled that she hadn’t even considered checking for this condition and set out to learn everything she could about it. She secured federal grants to study SCD in children and established protocols for routine screening for the disease. In 1976, she began a long association with the National Institutes for Health as a medical expert and later, as deputy branch chief of the Sickle Cell Disease Branch.
In 1986 Dr. Gaston published the results of a groundbreaking national study that proved the effectiveness of giving SCD children long-term penicillin treatment to prevent septic infections. Her study showed that babies should be screened for SCD at birth so that preventive penicillin could be given right away. The study resulted in Congressional legislation to encourage and fund SCD screening programs nationwide. Within one year, forty states had begun screening programs. One of the most important conclusions of her work was the ease with which the complications of Sickle Cell Disease could be avoided with early treatment, a life-saving practice that became a central policy of the U.S. Public Health Service.
In 1990, Dr. Gaston went on to become director of the Bureau of Primary Health Care in the U.S. Health Resources and Services Administration, the first African American woman to direct a public health service bureau, where she focused on improving health care services for poor and underserved families. She controlled a budget of $5 billion, serving 12 million patients. When Dr. Gaston retired in 2001, her staff presented her with newly received data from prophylactic penicillin programs recently carried out in Africa, underscoring the worldwide impact of her work.
Her scientific achievements, as well as her ongoing commitment to improving the health of poor and minority Americans, have been recognized in many awards and honors, including every award given by the Public Health Service, and the most prestigious honor awarded by the National Medical Association—the NMA Scroll of Merit, in 1999. She also received the NMA’s Lifetime Achievement Award and several honorary degrees and is celebrated on “Marilyn Hughes Gaston Day” in Cincinnati and Lincoln Heights, Ohio. The University of Cincinnati College of Medicine has named a scholarship in her honor, giving full medical scholarships to two underprivileged minority students each year. The scholarships help other young people facing discrimination and financial hardship to pursue their own dreams of a career in medicine.